Gonococcus and gonococcal infections. Reagent kit "Nutrient medium for isolation of gonococcus dry" (GNK agar) Medium for isolation of gonococcus dry
Laboratory methods are widely used in the diagnosis of diseases. genitourinary system sexually transmitted: gonorrhea, syphilis, trichomoniasis, etc. The presence of the disease requires measures to identify the cause of the infection.
Nutrient medium "SVG" is intended for the isolation and cultivation of gonococci in the study of material from a patient. Each kit is designed to prepare 110 ml of gonococcal medium ready for use.
Set composition
A set for obtaining a nutrient medium should be stored at a temperature of 2 - 8 ° C for no more than 12 months. Solid nutrient medium can be stored in test tubes or Petri dishes for no more than 7 days. The set for the preparation of a nutrient medium includes:
- base: agar, yeast extract, peptone, starch, salts;
- selective additive: coenzymes, erythrocyte lysate, antifungals, antibiotics, sugars;
- instructions for using the kit.
Methodology
The methodology includes several stages, each of which must be carried out in accordance with certain requirements. Upon completion of all stages of the diagnosis of the disease using the method of cultivating the pathogen on the gonococcal medium, the results are recorded after 24 hours, 48 hours and 72 hours. In acute gonorrhea, the growth of gonococcus is noted during the first day, in chronic gonorrhea - up to 72 hours.
The preparation of the base solution of the medium for cultural diagnostics is carried out by pouring the base into a container containing distilled water (100 ml) for subsequent swelling. The resulting suspension is placed in a water bath and periodically stirred until the base is completely dissolved, then the solution is boiled for 2 minutes. A solution of a selective additive is prepared by dissolving it in distilled water (10 ml) with stirring.
Ready nutrient medium is formed by adding the selective additive solution to the base solution. The resulting medium is poured into sterile Petri dishes. Before testing, the gonococcal environment must be maintained for one hour at a temperature of 37 ° C. Then the material is sown in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health "On the unification of microbiological (bacteriological) research methods used in clinical diagnostic laboratories of medical institutions."
The effectiveness of the bacteriological research method in
largely determined by the quality of nutrient media. AT
In our country, two types are most widely tested and used
nutrient media: ascites-agar and non-ascitic nutrient media.
Both media are based on meat-pentone agar (MPA) from meat
rabbits or fresh bovine hearts. The method of its preparation
is as follows. Rabbit meat is freed from fat and
tendons, passed through a meat grinder or chopped with a knife,
weighed, filled with double volume tap water and in such
the form is left in the refrigerator at 4° for a day for extraction.
Then the mass is heated to a boil, boiled for 10 minutes, cooled and
filtered through cheesecloth. To the filtrate add 2% agar-agar, 1%
peptone and 0.5% sodium chloride, heated until the agar-agar dissolves
and set pH = 7.5-7.6 (alkalinization is carried out by 20%
sodium hydroxide solution). The medium is brought to a boil, filtered
through a cotton-gauze filter, pour into sterile vials or
flasks and sterilized in an autoclave for 15-20 minutes at 0.5 atmospheres
pressure gauge (112ё).
The technique for preparing MPA from fresh bovine hearts is the same as
only boiling a mass of crushed hearts in water follows
produce 20 minutes instead of 10.
It is possible to prepare the basis of the nutrient medium without peptone.
In this case, the above method for preparing MPA is used, but
peptone is excluded from its composition, chopped rabbit meat is boiled
5 minutes instead of 10 and sterilize the medium in an autoclave for 10
minutes at 0.8 atmospheres on a pressure gauge (117ё).
Ascites agar
Ascitic fluid should be obtained from patients with
ascites due to heart failure, and
produced through a trocar into a sterile bottle and add 5% to it
chloroform for anesthesia. For 10 days, the liquid is mixed with
chloroform by rotating the bottle, then leave it at
room temperature until the chloroform completely settles to the bottom of the bottle
and clarification of the liquid. After that, as needed, transparent
ascitic fluid is poured into 50 ml sterile flasks with
cotton plugs and daily for 3 days they are placed in
water bath at 56 ° for 1 hour to evaporate chloroform
through a cotton plug. After checking the ascitic fluid for
sterility it can be used for enrichment
nutrient medium for the isolation of gonococcus at a concentration of 1/3 and 1/4
the volume of the medium, which is determined empirically.
Ascitic Media Recipes
1. MPA from rabbit meat or fresh bovine hearts
(рН=7.4-7.5) - 100 ml, casein hydrolyzate for parenteral
protein nutrition - 2 ml, yeast autolysate - 2 ml, whey
blood of cattle - 20 ml (Wednesday KDS-1).
2. MPA from rabbit meat or fresh bovine hearts
(рН=7.4-7.5) - 100 ml, 5% hemohydrolyzate solution - 2 ml,
yeast autolysate - 2 ml, bovine blood serum
cattle - 20 ml (GDS-2 medium).
3. MPA from rabbit meat or fresh bovine hearts
(рН=7.4-7.5) - 100 ml, medium 199 for tissue cultures without
antibiotics - 20 ml, yeast autolysate - 2 ml, blood serum
cattle - 20 ml (medium 199-SDS).
4. MPA from rabbit meat or fresh bovine hearts
(рН=7.4-7.5) - 100 ml, fresh chicken egg yolk - 10 ml,
blood serum of cattle - 20 ml (Wednesday ZhS).
Egg yolk is obtained sterile from dietary chicken eggs.
immediately prior to medium preparation. For this,
pre-treated with alcohol, the shell is opened with a sterile
with tweezers and the contents of the egg are poured into a sterile funnel. After
after the protein flows out, the yolk remaining in the funnel is transferred to
sterile dishes and a measuring pipette are taken necessary for
production of the nutrient medium volume of the yolk.
Preparation of yeast autolysate is as follows.
Baker's yeast is crushed and placed in a bottle exceeding
volume taken yeast 4 - 5 times, and leave for autolysis for two
days in a drying cabinet or thermostat at 60 °. Then thick
brown mass is diluted with a triple volume of warm tap water
water, mix well and centrifuge twice for 10 minutes at
1000 rpm (until the liquid becomes clear). supernatant
the liquid is drained, 0.5% sodium chloride is added to it, adjusted
pH to 7.4-7.5 and autoclaved for 30 minutes at 1 atmosphere for
manometer (120ё). Store in small containers in the refrigerator
Yeast autolysate can be replaced with a 1.5% solution
fodder yeast extract (EKD) in the same amount (2 ml) 1.5%
EPC solution is prepared in the laboratory from dry EPC by dissolving it in
sterile distilled water. Prepared this way
liquid extract is poured into sterile test tubes and sterilized in
autoclave at 0.5 barg for 20 minutes.
In all the above nutrient media, blood serum
cattle can be replaced by normal native
serum for bacteriological nutrient media, which
is the same serum, but with the addition of a preservative.
Preparation of the enriched medium
MPA, located in a vial or flask, is melted in water
bath, cooled to 56-58ё and add ingredients to it in
ratios indicated earlier in the recipes. Enriched with MPA at 3-3.5
ml is poured into sterile test tubes, the medium is slanted and moistened
0.5 ml sterile meat-peptone broth or isotonic
sodium chloride solution after it hardens. For check
for sterility, the medium is placed in a thermostat at 35-37o per day.
All of the above non-ascitic media, except egg, are transparent,
it is easy to differentiate colonies of microorganisms on them. Wednesday,
enriched with egg, differs in turbidity, it is yellow, grown on
her colonies, in particular, gonococci, are poorly distinguishable. However, growth
gonococcus is abundant on this medium and its colonies can easily be
detected by growth treatment with 1% solution
dimethyl paraphenylenediamine or other oxidase reagent,
which stains gonococcus colonies red, well
contrasting against the yellow background of the medium. The use of yolk
media without microbial growth treatment with an oxidase reagent
The quality of each new batch of laboratory culture medium
production must be checked by sowing on it
pathological material from patients in whom bacterioscopically
gonococci were found.
The shelf life of MPA in a refrigerator at 4o should not exceed 1
month, enriched environment - 7 days.
Due to the fact that for the above environment a short period of time is possible
storage, developed a method of manufacturing
lyophilized ascite-free nutrient medium, which is under
titled "Gonococcal isolation culture medium, dry"
available in two bottles: part I (medium base) and part II
(fortifiers). To prepare the working environment in part I
add 100 ml of sterile distilled water and heat
in a water bath at 100 ° until the contents of the vial are completely dissolved
(within 30 minutes). Extra time to withstand the environment in water
bath should not be, tk. this reduces its quality. Part II includes
24 ml sterile distilled water (dissolving enriching
substances occurs immediately). Then, subject to the conditions
sterility, part II is transferred to part I cooled to 56°,
mixed, poured into sterile test tubes, beveled and
moisturize as previously described.
Dry medium is prepared from rabbit meat or bull hearts,
in addition to those listed in recipe 1 (KDS-1 medium) enriching substances
it contains orotic acid at a concentration of 1 µg/ml. Wednesday
high quality, convenient for use in bacteriological
laboratories, because to convert a dry environment into a working one, it is required
only sterile distilled water.
The use of ascite-free nutrient medium with the addition
antibiotics and orotic acid gives good results with
bacteriological diagnostics, including extragenital
gonorrhea: gonorrhea of the tonsils and pharynx, rectum. Antibiotics
added to inhibit the growth of concomitant gonococcus
bacterial flora, which increases the growth rate of gonococcus,
facilitates the detection of its single colonies and isolation in pure
culture. Add 20.0 U/ml polymyxin M sulfate and 6.2 U/ml
ristomycin sulfate; instead of the latter, you can use
lincomycin hydrochloride - 2 μg / ml. Orotic acid is injected into
the composition of the nutrient medium in the amount of 1 µg/ml.
To do this, take a sample of orotic acid 1 mg (1000 μg) and
diluted in 1.0 ml of sterile distilled water (obtain
working solution containing 1000 mcg which can be stored in
refrigerator for 10 days) and sterilized in a water bath 15
minutes, then take 0.1 ml of the resulting solution and add to
100 ml enriched nutrient medium. Environment with antibiotics
must be used simultaneously with antibiotic-free medium
(one test tube with the medium with antibiotics, the other without them), because
although rare, there are strains of gonococcus that are sensitive to
the above antibiotics.
Storage medium (transport)
Composition of the preservation medium: 1) 1 liter of distilled water,
free from chlorine, 30 g of agar-agar; 2) 900 ml distilled
chlorine-free water, 2 ml thioglycolic acid, 12 ml 1M
sodium hydroxide solution, 100 ml of 20% aqueous sodium solution
monosubstituted phosphate, 20 ml of 1% chloride solution
calcium. The last mixture (2) is added to the freshly prepared
agar (1), adjust the pH to 7.3-7.4, pour 10 ml of the medium into
sterile test tubes, sterilized with flowing steam for 1 hour.
Cotton swabs on wooden sticks or rods made of
stainless steel with a diameter of about 2 mm, mounted in wadded
stoppers, boiled for 20 minutes in phosphate buffer, pH=7.4, and
impregnate for 24 hours in a 1% aqueous suspension finely
crushed charcoal. After drying, cotton swabs
correct, insert into bacteriological test tubes
of the appropriate diameter (equal to the diameter of the test tubes with the medium) and
sterilized in an autoclave for 20 minutes at 1 atmosphere (temperature
To prepare phosphate buffer, two solutions are prepared: 1
solution - 28.4 g of sodium are dissolved in 1 liter of distilled water
disubstituted phosphate (0.2M); 2 solution - in 1 l
distilled water dissolve 27.8 g citric acid(0.1 M).
Mix 181.7 ml of solution 1 and 18.3 ml of solution 2.
Seeding production using the save environment
is carried out as follows. Doctor examining a patient
removes a tampon from the test tube, introduces it into the focus of the disease on
a few seconds for soaking (you can do several
movements clockwise and counterclockwise), removes it without touching
surrounding objects, into a test tube with preservation medium. over
cotton plug, the test tube is closed with a rubber nipple. Before shipping
material to the bacteriological laboratory, the cultures are kept at 4
in the refrigerator for a minimum period, but no more than a day. Simultaneously
take pathological material and make smears for
bacterioscopic examination, which are sent to
laboratory along with culture. in bacteriological laboratory
immediately after receipt swabs with pathological material
removed from the storage medium and they are used to inoculate on the surface
slanted nutrient medium in test tubes. Each tampon is made
sowing on a nutrient medium in two test tubes. Seeding on the surface
nutrient medium should be made in zigzag movements
along the surface of the medium by rotating the swab. If the diameter of the test tubes
the preservation medium and growth medium is similar, you can swab
after inoculation, leave in the second test tube in contact with
nutrient medium. Crops are placed in a thermostat and grown at
36-37yo in a desiccator. It should be borne in mind that when using
preservation environment, the growth of gonococcus may occur later than with
direct sowing of pathological material on nutrient
Working with cultures
Gonococci can be grown in test tubes or
Petri dishes; The first method provides significant savings
environment. To increase the percentage of seeding of gonococci, seeded
nutrient media are placed in a thermostat in a desiccator with 20%
reactions between sulfuric acid and sodium bicarbonate: into a desiccator
a volume of 5 liters is placed glass with 50 ml of 10% sulfuric acid, in
Gonococci are bean-shaped, arranged in the form of diplococci, surrounded by a microcapsule, do not have flagella, do not form spores, similar to meningococci. The cell wall has an outer membrane, the proteins of which are divided into three groups according to their functional significance. Gonococci are characterized by the presence of pili, which differ from each other in their antigenic properties (16 antigenic variants). Gonococci are cultivated on nutrient media containing native protein (blood serum, ascitic fluid). Grow better at 3-5% CO2. On ascitagar they form transparent colonies with smooth edges. From carbohydrates, only glucose is fermented, catalase and cytochrome oxidase are formed - enzymes typical of Neisseria.Antigens
The antigenic structure of gonococci is variable. This is due to the presence of numerous antigenic variants of pili, which are formed during the development of infection.Pathogenicity and pathogenesis
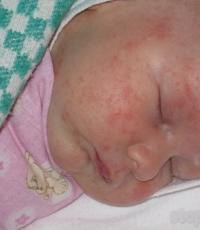
Gonococci are attached to the cylindrical epithelium of the urethra, the vaginal part of the cervix, rectum, conjunctiva of the eye, as well as spermatozoa and protozoa (Trichomonas, amoeba). Adhesion occurs due to pili and proteins of the outer membrane of the cell wall. characteristic feature gonococci is their ability to penetrate into leukocytes and multiply in them. Lipooligosaccharide part of the cell wall has a toxic effect. Capsular polysaccharides inhibit phagocytosis. Connecting with the villi of the cylindrical epithelium of the urethral mucosa, and in women and the endocervical canal, gonococci penetrate into the cells with the participation of proteins of the outer membrane of the cell wall. This leads to the development of acute urethritis, cervicitis and lesions in women of the cervix, appendages (tubes, ovaries), in men of the seminal vesicles, and the prostate gland. With extragenital localization, gonococci can damage the rectum and tonsils, and also cause blennorrhea (conjunctivitis) in newborns. Infection occurs during the passage of the birth canal of a mother with gonorrhea.Immunity
In gonorrhea, there is a humoral immune response. However, the resulting antibacterial antibodies do not have protective properties. During the course of the disease, IgA are formed that suppress the attachment of pathogen pili to the cells of the urethral mucosa. However, they are not able to protect the mucosa from subsequent infection by other generations of gonococci, which is associated with a change in their antigenic structure. This leads to reinfections and relapses, as well as to the transition of the disease to a chronic form.Gonococcal infections
The causative agent of gonorrhea and blennorrhea N.gonorrhoeae (according to the preliminary classification of gonococcus) belongs to the family Neisseriaceae, genus Neisseria. In smears from the secretions of patients, gonococci are shaped like coffee beans, gram-negative, located in pairs both inside leukocytes (incomplete phagocytosis) and outside the cells. According to their morphological features, they are very similar to meningococci. For gonococci, polymorphism is inherent - there are small and large cells, rarely rod-shaped. They are very whimsical to nutrient media. Grow better on media containing blood, serum, ascitic fluid. Gonococci contain protein and polysaccharide antigens, according to which they are divided into 16 serovars, but they have not yet been determined in routine bacteriological laboratories. For microbiological diagnosis of gonococcal infections, bacterioscopic, bacteriological, serological and allergic methods are used.Taking material for research
In order to adequately and benignly carry out bacteriological and bacterioscopic diagnostics, it is important to take the clinical material correctly. As a rule, it should be carried out by a doctor. In men, the discharge of the urethra, paraurethral passages, rectum is examined, if indicated, material from the oropharynx, as well as the secret of the prostate gland after its massage. You can also examine the sediment and "threads" of urine, but gonococci are detected in them much less frequently. Before taking material from the urethra, the patient should not urinate for 4-5 hours, do not use antimicrobials and disinfectant solutions. The external opening of the urethra is first wiped with a sterile cotton swab moistened with 0.85% sodium chloride solution, then with a dry swab. Smears are not made from manure, it flows freely, but from material taken by scraping from the mucous membrane of the urethra with a bacteriological loop or a special Volkmann spoon. With minor discharge, it is necessary to do a preliminary massage of the urethra. In women, the material is taken from the urethra, paraurethral passages, cervix, rectum, and, according to indications, from the oropharynx. First, the vagina is cleaned of secretions, the urethra is massaged, and the material is taken by scraping with a bacteriological loop or a Volkmann spoon. The cervix is first rubbed with a sterile cotton swab to remove the mucous plug. Discharge from the cervical canal is taken with a bacteriological loop or tweezers. The material from the distal rectum is taken using the Volkmann spoon in a blind way, i.e. without any preparation of the patient, or with the help of a rescope or rectal mirror. In this case, the studied material is taken directly from the visible site of the lesion. In oropharyngeal gonorrhea, mucus from the oropharynx is taken with sterile cotton swabs on special holders made of steel wire.For the diagnosis of "lenorrhea, the conjunctiva is removed with a bacteriological loop. Rarely gonorrhea is complicated by gonosepsis, endocarditis, arthritis. Then the blood or synovial fluid serves as the material for use. Taking into account the high - V resistance of gonococci to temperature fluctuations, the test materials are delivered to the laboratory in special thermoses or bags with a heating pad.Bacterioscopic examination
Bacterioscopic examination is the most common, although less sensitive method of laboratory diagnosis of gonorrhea and blennorrhea compared with the isolation of true cultures. This is especially true for the chronic course of the disease, when the test material contains a small amount of gonococci. However, with the correct sampling, repeated examinations of patients, the use of provocation methods, and a qualified assessment of smears, bacterioscopic examination quite often makes it possible to quickly and correctly diagnose the disease. Two thin, uniform smear preparations are made from the test material. One is stained with methylene blue, the second is stained by the Gram method. In the absence of methylene blue, one smear can be stained with a 1% aqueous solution of crystal violet or a 0.5% solution of brilliant green for 1 min. The conclusion about the presence of gonococci is made based on their properties: gram-negative color, diplococcal structure, shape of coffee beans, location inside leukocytes. Under the influence of antibiotics and other chemotherapy drugs, as well as in chronic gonorrhea, the morphology and color of gonococci can change. Individual cells take on a different shape and size (the so-called Asha shapes). In addition, gram-negative cocci similar to gonococci from the genus Veillonella can be found in the test material. This to some extent limits the diagnostic value of the primary microscopy method. The best and most reliable results are obtained by the immunofluorescence method. Thin smears from the secretions of patients are fixed in a burner flame. They are covered with fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled antigonococcal serum for 1 hour at 35°C in a humid chamber. After that, the smears are washed twice with a buffer solution, buffered with glycerol is applied and covered with coverslips. When gonococci interact with labeled antibodies under a fluorescent microscope, a characteristic glow around bacterial cells is visible.Bacteriological research
Indications for the isolation of pure cultures of gonococci are repeated negative results of bacterioscopy, the presence of suspicious gonococci, but not morphologically identified microorganisms, as well as for a reliable establishment of the cure of the disease. It is very important to immediately place the crops in the thermostat. If it is impossible to carry out crops at the place of taking the material, you can hang it with a cotton swab in a test tube with Stewart's transport medium, which ensures the viability of gonococci during delivery to the laboratory. Crops are carried out according to the standard scheme in one of the special nutrient media in test tubes or Petri dishes (KDS, Bailey , blood or serum agar, dry nutrient medium of the Kharkov enterprise "Biolek" for the production of bacterial and medicines ). For diagnostic cultivation of gonococci in many countries, "chocolate" agar is also used. The best are media made on the basis of agar from rabbit meat or fresh bovine hearts. The addition of 20 U/ml of polymyxin and 2 µg/ml of lincomycin to them significantly increases the frequency of seeding of gonococci, since these drugs inhibit the growth of other bacteria. All media before sowing are heated in a thermostat for 15-20 minutes. Cups and tubes with cultures are placed in desiccators, where an atmosphere with 20% CO2 is created. Colonies usually grow in 18-24 hours, but late growth is also possible. Then the crops are kept in a thermostat (in a desiccator!) Up to 8 days, checking the appearance of growth daily. Gonococcal colonies that have grown have a round, slightly convex shape, smooth edges, a shiny surface, and a mucous consistency. They are transparent, like dewdrops, almost colorless, although whitish variants can also occur. The resulting colonies are examined macro- and microscopically. In smears, gonococci are located in pairs, tetrads and clusters. Representative colonies are plated on a serum agar slant to isolate a pure culture. The final identification is carried out taking into account the morphological, culture, enzymatic and antigenic properties. Biochemically, gonococci are not very active. On serum media with 1.5% of various carbohydrates, they decompose only glucose, but not maltose and sucrose. The oxidase activity of isolated cultures is determined by applying a 1% solution of dimethyl paraphenylenediamine to the colonies (after microscopy). Oxidase-positive colonies first turn red and then turn black. Differentiation of gonococci from other species of the genus Neisseria is of particular importance in the diagnosis of oropharyngeal gonorrhea. As you know, on the mucous membrane of the tonsils, oropharynx and nasopharynx there is constantly a large number of gram-negative Neisseria - representatives of the normal human microflora. Reliable methods for identifying gonococci are immunofluorescence, latex and coagglutination tests, as well as determination of enzymatic properties. Be sure to conduct a qualitative determination of the sensitivity or resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics using the agar diffusion method using discs. In order to increase the frequency of finding gonococci in smears during primary microscopy and more reliable isolation of pure cultures, especially in cases of a sluggish, chronic course of the disease, gonorrhea provocation methods are resorted to. , that is, an artificial exacerbation of the pathological process, as a result of which large quantity gonococci. The main of these methods are: a) chemical - instillation into the urethra of a 0.5% solution of silver nitrate in men, lubrication of the cervical canal with 2-5% solution of silver nitrate; b) mechanical - the introduction of a direct bougie into the urethra for 10 minutes, or holding anterior ureteroscopy; c) biological - intramuscular administration of gonovaccine in the amount of 500 million microbial bodies or pyrogenal 200 MPD; d) alimentary - consumption of salty, spicy food; menstruation. It is even better to combine several methods of provocation, for example, chemical, alimentary and biological. Recently, for a more reliable detection of the causative agent of gonorrhea, polymerase chain reaction. It allows you to identify the pathogen in cases of chronic gonorrhea, when bacterioscopic and bacteriological examination does not give positive results.Serological diagnosis
Serological diagnosis of gonorrhea is carried out relatively rarely, mainly in its chronic course, when bacterioscopic and bacteriological studies do not give positive results. AT modern conditions ELISA, RNGA and Borde-Gangu reaction (RSK) are carried out. The antigens for these reactions are: heat-killed polyvalent gonococcal vaccine, ultrasound-inactivated vaccine, protein and polysaccharide fractions of gonococci, and pyridine antigen. ELISA and RNHA are highly specific and reliable serological tests. Compared to the past, the RSK has somewhat lost its role. It is of no practical value in the diagnosis of acute gonorrhea, since it is treated before a significant amount of antibodies is formed. To establish the reliability of the cure, it is generally unsuitable. The Borde-Jangu reaction is important in the serodiagnosis of chronic gonorrhea, especially in its complicated forms (gonosepsis, metritis, prostatitis arthritis, etc.). The diagnostic value of allergic tests is somewhat devalued by the fact that they are positive for many years after suffering gonorrhea. For their production, 0.1 ml of fresh gonococcal vaccine (100 million microbial cells in 1 ml) is injected intradermally. After 24 hours, hyperemia is observed, sometimes with edema in the center.Treatment and prevention
For chemotherapy of gonorrhea, antibiotics are used: beta-lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins) and other antibiotics. Vaccination of gonorrhea is not carried out due to the lack of effective vaccines. To prevent blennorrhea, all newborns are instilled with a solution of one of the listed antibiotics on the conjunctiva of the eye.This agar supplemented with blood, hemoglobin or other additives is recommended for the selective isolation of gonococci.
Compound**:
** The composition is verified and brought to compliance with the necessary parameters
Cooking:
Suspend 7.2 g of powder in 100 ml of distilled water to prepare a double strength medium. Heat to a boil to completely dissolve the particles. Sterilize by autoclaving at 1.1 atm (121°C) for 15 min. Cool to 50°C and aseptically add separately prepared 100 ml of 2% sterile hemoglobin solution (FD022) and GC supplement (FD021). Mix thoroughly and pour into Petri dishes. To impart selective properties to the medium, you can add antibiotics included in the following additives: VNC (FD023), VCNT (FD024), Linco T (FD026), Vanco (FD028).
For the preparation of chocolate agar, a standard concentration medium is prepared by mixing 3.6 g of the powder in 100 ml of distilled water. Sterilize, add up to 5% (v/v) of sterile defibrinated blood, and heat the medium at 80°C for 10 min.
Principle and evaluation of the result:
This agar supplemented with blood or hemoglobin and other additives is recommended for the selective isolation and cultivation of fastidious microorganisms such as gonococci and Haemophilus influenzae. Johnston developed chocolate agar that could grow within 24 hours. Neisseria gonorrhoeae(one). Later, other authors (2) improved the medium by introducing hemoglobin into its composition.
Agar contains a special peptone - a source of nutrients for microorganisms. Starch neutralizes toxic substances formed by Neisseria, and phosphates counteract the pH shift resulting from the formation of amines, which can also affect the growth and viability of microorganisms. Hemoglobin serves as a source of factor X for hemophilic bacteria. Another additive enriches the medium with factor V (NAD, nikoninamide adenine dinucleotide), necessary for Haemophilus influenzae, as well as amino acids, vitamins, iron ions, etc., which stimulates the growth of pathogenic neisseria.
Do not use cotton swabs to collect material. Sowing is carried out immediately after the selection of the material. It must be done so that there are zones of dense and rare growth. Seeding is incubated at 37°C in an atmosphere of 5-10% carbon dioxide and 70% humidity. All suspicious colonies should be checked in biochemical and/or serological tests.
Quality control:
Powder Appearance:
Homogeneous free flowing light yellow powder.
Finished medium density:
A medium is formed, corresponding in density to a 1.0% agar gel.
Color and transparency of the finished medium:
The base of the medium is light yellow, transparent or slightly opalescent. After the addition of hemoglobin, the medium becomes chocolate brown and opaque if a gel forms in the Petri dishes.
Acidity of the environment:
At 25° C., an aqueous solution (3.6% w/v) has a pH of 7.2 ± 0.2.
Cultural properties:
Growth characteristics of the reference strain after 40-48 hours at 35-37°C on chocolate agar, prepared on this basis, in the presence of 5-10% carbon dioxide and 70% humidity in the atmosphere.