L-Threonine Threonine - Daily Value. L-Threonine Deficiency Threonine
2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
Chemical properties
Threonine - , the molecule of which contains two chiral complex , has 4 optical isomer . There are 2 isomer D- and 2 isomer of L-threonine.
Molecular weight of the compound = 119.1 grams per mole. The melting point is about 256 degrees Celsius. Chemical formula Threonine C4H9NO3.
Usually, the substance is part of various biologically active food supplements and medicines, as well as lysine, methionine and other components. By her own amino acid - white crystalline powder, odorless. Bacteria and plants, unlike humans, can independently synthesize a substance from aspartic acid .
pharmachologic effect
Metabolic.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Amino acid Threonine is indispensable for the human body, takes an active part in the synthesis of protein structures. A person needs to consume half a gram of a substance per day, children - about 3 grams.
Most threonine is found in dairy products, nuts, legumes, and eggs. Entering the body, the substance is quickly and completely metabolized.
Indications for use
Preparations containing this amino acid are prescribed:
- to provide full or partial parenteral nutrition;
- as a prophylactic for the loss of proteins;
- at injuries, polytrauma, burns, peritonitis, sepsis, multiple organ failure , as part of complex therapy;
- to maintain the body after major operations;
- with inflammatory bowel diseases;
- for treatment cachexia ;
- with a decrease in mental performance and concentration due to malnutrition or during periods of active growth;
- alcoholics for withdrawal withdrawal syndrome or to maintain remission.
Contraindications
The tool is contraindicated:
- at shock, hypoxia, decompensated heart failure ;
- with violations of the processes of amino acid metabolism;
- persons with metabolic acidosis ;
- children under 2 years old;
- with severe kidney disease, in the absence of hemofiltration or dialysis ;
- patients with severe liver failure.
Side effects
The substance is most often well tolerated by patients. Rarely: dizziness, nausea.
Threonine, instructions for use (Method and dosage)
Depending on the dosage form and the type of disease, the dosage and mode of administration are very different.
The tablet form is taken sublingually , using a solution and emulsions, intravenous infusions are performed at different rates of administration and dosage.
Today, everyone knows how important compounds called are for our body. One such compound is threonine. And although it is part of almost all the human body, threonine is not synthesized in the human body. That is, it comes to us only with food or with food additives. This amino acid is especially important for children, their need for threonine is greater than for an adult.
Why is threonine useful for us? Most importantly, it is necessary for the synthesis of the amino acids serine and glycine, which in turn are involved in the synthesis of collagen and elastin, the proteins of connective and muscle tissue. and elastin are necessary for muscles, and for tendons, and for ligaments, and for the elasticity of blood vessels, skin, and normal heart function. Naturally, children need threonine in larger volumes than an adult, because their body is just being built. If not enough building material it is possible to develop problems with the spine - scoliosis, dislocations of the cervical vertebrae, with muscles - flat feet, muscle dystrophy, with teeth - the development of caries, with nails, hair. Perhaps even visual impairment. An adult also needs threonine, as an adult's body is constantly updated. And for a good condition of the skin or teeth (and threonine is part of the tooth enamel), you need a constant intake of threonine in the body.
Increased doses of this amino acid are necessary for recovery after operations and various injuries.
Threonine is also essential for healthy liver function. In combination with methionine and aspartic acid, it takes care of the processing of fats and fatty acids. This means that it prevents the development of fatty liver disease - hepatosis.
Threonine is also needed for the normal functioning of the digestive tract. It is part of some digestive enzymes, such as pepsin, which is responsible for the breakdown of proteins in the stomach.
Threonine supports the functioning of the body's immune system, promotes the elimination of toxic substances, therefore it is very important during pregnancy - it reduces toxicosis in the early months.
It is used in the treatment of diseases of the central nervous system, depression, improves mood, increases concentration, and performance. Threonine is also used in the treatment of alcoholism and drug addiction.
Vitamins B3 and B6, as well as the trace element magnesium, contribute to the absorption of threonine by the body. For a full-fledged high-quality muscle protein, threonine must be consumed in combination with methionine and aspartic acid.

As a rule, there should not be a lack of threonine with good nutrition, but if a person consumes a small amount of protein foods (meat, fish, mushrooms), a lack of this important amino acid can manifest itself in muscle weakness, depression, hair loss, bad condition skin, nails and teeth, developmental delay in children. The lack of threonine leads to a lack of all amino acids for the synthesis of which it is necessary. In medical practice, cases have been recorded when threonine is not absorbed by the body. Then, for treatment, increased doses of glycine and serine, which are formed as a result of the synthesis of threonine, are prescribed.
Excess threonine in the body leads to the accumulation of uric acid. When using nutritional supplements with this amino acid, it is necessary to monitor this, since both excess and deficiency of threonine is harmful to our health.
What foods contain threonine? In protein products - meat, poultry, eggs, cheese, fatty sea fish, seafood, and mushrooms. Plant food also contains threonine, but in smaller quantities, it is present in lentils, beans, wheat, rye, buckwheat, and nuts. Threonine deficiency can be experienced by vegetarians who limit the consumption of animal foods.
The daily requirement of threonine for an adult is 0.5 g, for children - 3 g. The need for threonine increases with the active growth and development of the body, with increased physical activity, during sports, in depressive states, and, as we have already said, vegetarianism. But with age, the need for threonine decreases.
For athletes, this amino acid is of great importance, as it promotes growth and
- hydroxyamino acid, for humans, threonine is an essential amino acid.
The threonine molecule contains two chiral centers, which determines the existence of four optical isomers. However, the name L-threonine is used for one diastereomer, 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid. The second stereoisomer, rarely found in nature, is called L - allothreonin. The two remaining isomers D-threonine and D-allotreonine are only of minor importance.
Being an essential amino acid, threonine is not synthesized in the human body, and its supply is replenished only from threonine-containing proteins in our food. In plants and microorganisms, threonine is synthesized from aspartic acid via α-aspartyl semialdehyde and homoserine.
Functions of threonine in the human body
Threonine is an important amino acid that contributes to the normal development of the body; together with other proteinogenic amino acids, it is involved in the formation of natural proteins.Threonine also supports the functioning of the liver, cardiovascular, central nervous and immune systems.
Threonine is necessary for the biosynthesis of the amino acids glycine and serine, which, in turn, are responsible for the production of collagen (the basis of the body's connective tissue), elastin (the protein responsible for the elasticity of connective tissues) and muscle tissue. Threonine helps connective tissues (tendons, bones, cartilage, dermis) and muscles become strong and elastic, including threonine affects the heart muscle (heart), where it is found in significant quantities. Threonine helps build strong bones and tooth enamel, and can speed up wound healing and recovery from injury.
Threonine in combination with and amino acids aspartic acid help the liver perform lipotropic functions (break down fats and fatty acids). Without enough threonine in the body, fats can accumulate in the liver and eventually lead to liver failure.
Threonine supports the immune system by aiding in the production of antibodies. Threonine is used to treat a variety of disorders of the nervous system, and may be useful in the treatment of some types.
Threonine supplementation may be useful in the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig's disease or Charcot's disease, because L-threonine increases glycine levels in the central nervous system. Studies show that the symptoms of another disease - multiple sclerosis(MS), which affects nerve and muscle function, can be reduced with threonine supplements. A study conducted in 1992 showed that taking 7.5 g of L-threonine daily reduced muscle spasticity in the observed study participants.
Sources of Threonine
The daily requirement for threonine for an adult is 0.5 g, for children - about 3 g.Foods high in threonine:
- 3.685 g
Spirulina, dry - 2.970 g
Trumpeter - sea mollusk - 2.136 g
Veal - 1.604 g
Pork - 1.512 g
Beef - 1.423 g
Turkey - 1.330 g
Anchovy fish, canned in oil - 1.266 g
- 0.736 g
- 0.328 g
- 0.158 g
- 0.107 g
Dairy products, meat, grains, mushrooms, and vegetables contain threonine, so threonine deficiency is unlikely with a well-balanced diet. However, vegetarians may benefit from threonine supplements, as meat is an excellent source of this amino acid today. The content of threonine in cereals is very low.
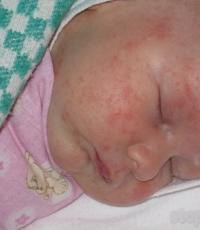
Symptoms of threonine deficiency include emotional arousal, confusion, digestive difficulties, and fatty liver.
Threonine is available in protein supplements such as protein powder and amino acid tablets. The standard daily dose is 103 to 500 milligrams. Exceeding the recommended dose of threonine can impair liver function and lead to the formation of large amounts of toxic urea and ammonia in the body.
Threonine. Side effects and safety
Threonine is safe at a dose of 2-4 g per day for up to 12 months. Some people, when taking threonine, experience minor side effects such as indigestion, nausea, and skin rashes.Information about the use of threonine during pregnancy and breastfeeding not enough. Just in case, stop taking threonine during pregnancy and lactation.
There is some concern that threonine may lead to decreased lung function in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). In one study, patients taking 4 grams of threonine per day experienced significantly reduced lung function compared to patients who did not receive threonine. But to determine that threonine was actually to blame, evidence is needed.
Threonine reduces the effectiveness of drugs used for treatment (NMDA antagonists), in particular, the effectiveness of the drug memantine (Namenda) is reduced.
Opening L-threonine fell on 1935. This is an essential monoaminocarboxylic amino acid, which is found in the muscles of the skeleton, heart, and in the cells of the central nervous system. It is needed to maintain good immunity. The substance is not produced by the body, but is found in food: meat, eggs, sea fish, beans, nuts, buckwheat, mushrooms, etc.
There are amino acid isomers: D-, L- allothreonine, as well as D-, L- threonine. The latter is considered the most valuable for the body, as it takes part in the formation of proteins, is integral part elastin and collagen. This is a substance that helps preserve the enamel on the teeth. To improve the digestibility and absorption of threonine, you should also eat foods rich in B vitamins and magnesium.
Threonine Health Benefits
Threonine brings the following benefits to the body:
- Favorably affects the digestive system, fights gastric ulcers.
- Reacting with methionine and aspartic acid, it leads to the breakdown of fats that accumulate in the liver.
- The use of this amino acid leads to relaxation and calmness, therefore it effectively fights depression.
- Promotes healing of wounds, scars, raising muscle tone.
- Supports immunity, contributes to the proper functioning of the heart and central nervous system.
- Included in proteins and enzymes.
- Maintains the beauty of nails and hair.
- Protects the skin from dryness, helps smooth out wrinkles, is part of many cosmetics.
Threonine for athletes
Threonine is used as a dietary supplement in sports nutrition. Athletes need it for:
- muscle strengthening;
- increase endurance under heavy loads;
- fast recovery after training.
What causes a lack of threonine?
Lack of this amino acid is rare, and manifests itself in the following:
- Tooth enamel deteriorates, hair falls out, nails become brittle, skin loses turgor.
- It becomes difficult to concentrate.
- There is depression, anxiety, oppression.
- Muscle mass is lost.
- There is weakness in the muscles.
- Children have growth retardation.
Daily allowance and side effects
Threonine should be taken at 0.5 g per day. If too much threonine accumulates in the body, this leads to an excess of uric acid, which can negatively affect the functioning of the liver and kidneys.
The product is not a drug.
We do not recommend the use of products by persons under 18 years of age.
Before you start taking any product, be sure to consult a specialist!
Threonine is an important amino acid. It enters the body with food - legumes, fermented milk products, brewer's yeast, chicken eggs, meat and fish. With a lack of a substance, it is obtained with food additives.
Threonine is an important amino acid, with a lack of a substance, it is obtained with food additives.
Role in the body
The amino acid has the following pharmacological actions:
- Participates in the formation of protein compounds. It is especially necessary for building tooth enamel, collagen and elastin fibers.
- Promotes the breakdown of fats. With a lack of this substance, the deposition of fat in the liver is observed.
- Normalizes blood glucose levels. In the liver, the amino acid is converted to glucose. This process is called gluconeogenesis.
- Promotes tissue repair after injury. The level of the substance in the blood of patients with fractures, wounds and burns is several times higher than the norm. Taking threonine preparations helps speed up the healing process.
- Relieves muscle spasms. Numerous studies have confirmed that the substance improves the condition of the patient with multiple sclerosis.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Threonine preparations are necessary for the construction of protein structures. The human body requires at least 3 g of this amino acid. Upon entering the intestine, the active substance is rapidly absorbed and excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolites.
Indications for the use of threonine
L-threonine preparations are used:
- if necessary, full or partial intravenous administration of nutrients;
- to prevent the loss of protein components;
- with injuries, fractures and burns;
- with general blood poisoning;
- in the prevention of dysfunction of internal organs;
- as part of the complex treatment of hepatic, renal and heart failure;
- to speed up the recovery process after major operations;
- with inflammatory changes in the intestinal mucosa;
- for the treatment of depletion of the body;
- with a decrease in intellectual abilities and a deterioration in concentration with a lack of oxygen and nutrients;
- during active bone growth;
Essential amino acids. Threonine
Vegetarianism - harm or benefit: Threonine
Threonine for alcoholism
The active additive is effective in the treatment of alcoholism. It reduces cravings for ethyl alcohol, prolongs the period of refusal to drink in drunken alcoholics, reduces the severity of the withdrawal syndrome. Regular intake helps to avoid the destruction of liver cells and the development of cirrhosis.
Contraindications
Threonine preparations are contraindicated in:
- decompensated renal, hepatic and heart failure;
- violation of amino acid metabolism;
- metabolic acidosis;
- early childhood patient (up to 2 years);
- severe pathologies of the kidneys, accompanied by a violation of dialysis and hemofiltration;
- oncological diseases of the liver.
Side effects of Threonine
The substance is well tolerated by the human body. Sometimes the following side effects may occur:
- pain in the middle of the abdomen;
- nausea and vomiting;
- heartburn;
- allergic reactions in the form of skin rashes;
- headaches;
- dizziness;
- increased sweating;
- stomach upset.
Overdose
There have been no reports of overdose. With prolonged consumption of high doses of drugs containing amino acids, digestive problems may occur.
Features of use
The dosage depends on the individual characteristics of the patient, the scope and dosage form of the drug. Tablets are placed under the tongue, solutions and emulsions are administered intravenously through droppers. The rate of administration is selected individually.
For kids
For children, d-threonine preparations are prescribed for high physical and mental stress. Children under 8 years old take the drug 1 time per day, patients 8-14 years old - 2 times, adolescents 14-18 years old - 3 times a day. Therapeutic course - 2 weeks. With caution, drugs are prescribed to children with genetic pathologies, diabetes Type 1, phenylketonuria. Treatment with the drug is combined with constant monitoring of blood sugar levels, changing the dosages of insulin and hypoglycemic agents.

For adults
To improve performance, threonine preparations are taken 3 times a day for 12 days. In the complex treatment of alcoholism, tablets are prescribed 2 times a day. Therapeutic course - 2 weeks.
Where is it contained?
Preparations analogues
- Aminoven Infant (solution for intravenous administration);
- Aminosol-Neo (10% solution for infusion);
- Biotredin (tablets for sublingual use);
- Gepasol-Neo (8% solution for intravenous administration);
- Kabiven (emulsion for administration via droppers)
- Ketoaminol (film-coated tablets);
- Ketosteril (tablets);
- Moriamin Forte (capsules).
Products containing threonine
Amino acids are found in the following foods:
- quail and chicken eggs;
- grouse meat;
- veal;
- lamb;
- turkeys;
- Chicken;
- mushrooms;
- sea fish;
- wheat bran;
- cheese.
Threonine in sports nutrition
Amino acids play an important role in sports nutrition. It stimulates the growth and development of muscle tissue, strengthens skeletal muscles, increases the body's endurance during training. When taking threonine preparations, a person quickly recovers from injuries sustained during sports. The substance is necessary for people involved in weightlifting, swimming, running, bodybuilding.
Interaction with other substances
Threonine preparations can be taken in combination with methionine and aspartic acid. The effectiveness of the substance increases when it is used together with vitamin B3 and nutritional supplements containing magnesium. Information about interactions with others medicines not received.