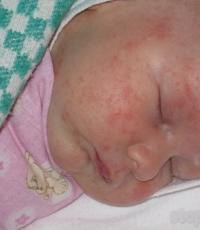
Barrier adaptations of the organism providing passive resistance. Reduced resistance to infections - causes and diseases
Despite the importance of vaccines in saving the livestock of dogs, it must be borne in mind that this specific agent is not always able to prevent infectious animal diseases. The main reason for this is a decrease in the overall resistance of the organism, or, in other words, the immune deficiency of animals. Immune deficiency is expressed in the fact that the dog's body is not able to respond properly to the introduction of vaccines, i.e., to develop antibodies against the pathogen, or in the fact that the already formed immunity decreases under the influence of adverse factors and cannot be an obstacle to the development of infectious diseases. Immune deficiency is congenital, age-related and acquired.
Congenital immune deficiency is associated with the hereditary inability of animals to a full-fledged immune response. A decrease in the resistance of an organism of this type is almost impossible to correct. Therefore, such disorders can be prevented only by selecting healthy parental couples with normal immune protection.
Age-related immune deficiency occurs in early and old age, and if in the first case it is associated with the underdevelopment of the immune system, then in the second - with its deterioration.
Acquired immune deficiency occurs with severe diseases of various origins, prolonged exposure to drugs, extensive surgical injuries, neoplasms, in which there is a large loss of protective factors and structural and functional changes appear in the immune system. The development of this type of immune deficiency contributes to inadequate feeding (lack of proteins, vitamins, minerals in the diet).
Quite often, the cause of acquired immune deficiency is stress. Stress is a tense state of the body that occurs under the influence of unusual, strong influences on the animal. Stress is not always harmful to animals. Only extreme, prolonged or frequently repeated exposures have a negative effect. Numerous adverse environmental factors that can cause stress can be divided into physical (temperature and humidity conditions, noise, prolonged mechanical stress, physical overstrain, strong solar radiation, etc.), chemical (harmful gases, chemicals, including medications), biological (abrupt changes in feeding, intensive use in breeding, early weaning of puppies) and emotional-psychological (fright, excessive stress during training, veterinary measures, change of owner, transportation, acquisition of livestock, etc.).
Leukocyte plasma is a universal non-specific agent for the elimination of immune deficiency in dogs. Leukocyte plasma is made from the blood of dogs, therefore, all biologically active substances that make up its composition (proteins, peptides, enzymes, antibodies, hormones, etc.) are not alien to animals within this species (i.e., for dogs), do not cause any adverse reactions. The homology (family resemblance) of plasma components in relation to the internal environment of the dog's body determines it more effective action compared to other tissue biostimulants. In addition to increasing the immunological activity of leukocyte plasma improves the trophic functions of the body, accelerates regeneration processes. The drug has bactericidal and inactivating properties against many bacteria and viruses, has a beneficial effect on the growth and development of puppies.
Leukocyte plasma is administered prophylactically to adult dogs and puppies subcutaneously or intramuscularly at a dose of 0.2 ml/kg of animal weight two or three times with an interval of 7 days. The protective effect, expressed in an increase in the body's resistance to various diseases and neuropsychological stress, persists for 2-3 months after these procedures. It is recommended to administer the drug to puppies in the first half of pregnancy.
In the absence of leukocyte plasma, to increase nonspecific immunobiological resistance, you can use stabilized (using sodium citrate or Trilon "B") blood from healthy adult dogs or horses at a dose of 3–5 ml subcutaneously or intramuscularly two and three times with an interval of 2– 3 days. The effectiveness of stabilized blood is significantly increased if it is kept for 4–5 days in a refrigerator at a temperature of 2–4 ° C before use.
Recently, thymus (T-activin, thymosin) and bone marrow (B-activin) preparations have been prescribed as adaptive stimulating therapy for age-related and acquired immunodeficiencies. These drugs are administered subcutaneously at a dose of 0.5–1 ml once a day for 3–5 days in a row.
For the same purpose, nonspecific immunoglobulin (at a dose of 2-3 ml per kg of body weight orally, at a dose of 0.5-1.0 ml per kg of body weight subcutaneously or intramuscularly 1 time per day for several days), hydrolysin ( 1 ml per kg body weight subcutaneously or intramuscularly two or three times with an interval of 7 days), protein hydrolysates, aminopeptide (0.1–0.2 ml per kg body weight intramuscularly or subcutaneously two or three times with an interval of 7 days), Dorogov's Stimulant Antiseptic (DSA), fraction 2 (0.5–2 ml per head orally once a day for 5 days), sodium nucleonate (2–3 mg per kg body weight orally once a day for 2–3 weeks.
Good results are obtained by the prophylactic use of adaptogens of plant origin: eleutherococcus extract, radiola extract 10-12 drops (5-10 drops for puppies) 1 time per day (before meals), as well as other similar drugs.
An important point dog disease prevention is good nutrition. Puppies are especially sensitive to nutritional errors. The diet of puppies and whelping bitches must include meat, dairy products, eggs. As a mineral supplement, it is best to use bone meal (for puppies 5-8 g, for adult dogs 15 g, per day with food) - in it all the necessary substances are in a balanced state. With a clear lack of calcium and phosphorus (rickets, general weakness), calcium gluconate (1-3 g or 2-6 tablets 2 times a day) and calcium glycerophosphate (0.25-0.5 g or 1-2 tablets 2 times a day) can be given. in a day).
Vitamins A, D, E, C, B have a pronounced stimulating effect: g and others. Vitamins are best used in combination, since this enhances the physiological effect of each of them. Widely used multivitamin preparations are undevit, dekamevit, revit, etc. Adult dogs are usually given 1 tablet, puppies - 1/2 tablets 1 time per day for 20-30 days. Oily multivitamin preparations - trivit, tetravit are well absorbed by dogs. They can be injected intramuscularly (0.5-3 ml twice with an interval of 7 days) or given orally (1-5 drops 1 time per day for 20-30 days).
The above measures prevent all types of immune deficiency, including those caused by one or another stress factor. However, in the case of psycho-emotional stress, the excited and anxious state of animals is best relieved with the help of sedative drugs: chlorpromazine (0.5-1.0 mg per kg of animal weight subcutaneously, intramuscularly or orally 1 time per day), pipolfen (1 mg per kg of animal weight intramuscularly or orally 1 time per day), etc. Psychotropic drugs begin to be used in 30-60 minutes. before the onset of stress factors (for example, surgery, transportation, change of owner, etc.) and, if necessary, then used during the initial period of adaptation to new conditions (no more than 1–2 weeks).
Recently, in many regions of the country bad influence dog immunity is affected by chemical and physical stress factors associated with environmental pollution of water, air and food, increased radiation. To prevent immune deficiency of this nature in adult animals, the above-mentioned means are sufficient. Puppies, due to their greater vulnerability to diseases, are additionally recommended to prescribe a special detoxification-immunostimulating course of treatment. Such a course should be carried out twice: in the suckling period (from 15 days of age) and after weaning (before vaccination).
Unithiol - 0.5–1 ml of 5% solution intramuscularly or orally with a pipette or syringe. The drug is applied three times 1 time per day with an interval of 1 day;
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) - 1-2 ml of 5% solution intramuscularly or 50-100 mg (1-2 tablets) orally as an aqueous suspension 1-2 times a day for 5 days;
Indomethacin - 1/4 of the tablet is given orally in crushed form with milk 1-3 times a day for 10 days;
Tocopherol acetate (vitamin E) - 1 drop of 30% solution or 3 drops of 10% solution once a day for 7 days;
Decaris - crush 1/10 of a tablet (about 5 kg) and inject with water into the rectum using microclysters.
An important factor affecting the overall resistance of the body of dogs and especially puppies is the illumination of their places of detention with natural or artificial light. The optimal mode of illumination contributes to the activation and maintenance of the protective properties of the body at a sufficiently high level. With a lack of natural light, artificial lighting (incandescent lamps, fluorescent lamps), as well as dosed ultraviolet irradiation (mercury-quartz or erythentic lamps) should be used.
It is innate in origin. It includes barriers between the external and internal environment, cellular and humoral factors of the internal environment and is provided by the following mechanisms.
Barriers between the external and internal environment- skin and mucosal epithelium (oral cavity, nasopharynx, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, eyes, urinary tract). Their barrier function is provided mechanically, i.e. an obstacle to passage, removal due to the flickering of the cilia of the epithelium and the movement of mucus, as well as due to chemicals released by the cells of the barriers. The skin secretes bactericidal substances (lactic and fatty acids, formation of hydrogen peroxide) as part of the secretions of the sweat and sebaceous glands. Hydrochloric acid and gastric juice enzymes destroy microorganisms. Lysozyme of saliva, lacrimal fluid, respiratory mucus, blood, mother's milk, synovial, peritoneal and pleural fluids has a powerful bacteriolytic effect.
At the same time, the secrets of the mucous membranes also contain specific protection factors, for example, immunoglobulins JgA - secretory antibodies.
Humoral factors of the internal environment are plasma proteins.
fibronectin- a protein that, when attached to foreign particles, cells, microorganisms, facilitates phagocytosis, i.e. it is one of the opsonization factors. It is produced by macrophages, endothelium, smooth muscle cells, astroglia, Schwann cells, enterocytes, hepatocytes and other cells. It has a high affinity for fibrin, actin, heparin.
Interferons produced by neutrophils and monocytes. They have various functions: they stimulate the activity of natural killers and macrophages, directly affect DNA and RNA-containing viruses, inhibiting growth and activity, retard growth and destroy malignant cells, possibly through increased production of tumor necrosis factor. They are divided into 3 groups: a-, b- and g-interferons, the latter being immune (produced in response to an antigen). g-inter-
feron, produced by natural killers and activated T-helpers, activates macrophages (stimulates their production of interleukin-1), enhances the production of superoxide radicals in neutrophils. Interferons are used in clinical practice. Interferon-a activates the differentiation of leukemia cells to mature forms, modeling their genetic program with blocking the autocrine production of growth stimulants and their receptors in these cells. Therefore, it is effective in the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (hair cell leukemia).
Lysozyme is an enzyme produced by neutrophils and macrophages. It destroys the membranes of bacteria, promoting their lysis. Lysozyme stimulates T-, B-lymphocytes, enhances the adhesion of immunocompetent cells, activates the complement system, affects various stages of phagocytosis, chemokinesis, opsonization and antigen degradation. Lysozyme also stimulates regenerative processes in tissues, enhances the action of antibiotics. Determination of its activity is a way to assess the state of nonspecific resistance.
Complement- an enzyme system of more than 20 globulin proteins. They are denoted by the letter C with a serial number (C 1, C 2, C 3, etc.). These proteins are produced by macrophages in an inactive state. Activation occurs either due to the contact of the system components with any foreign cell, or with the antigen-antibody complex. Complement is characterized by the following functions: cytolysis (destruction of foreign cells), opsonization (facilitation of phagocytosis), participation in the development of inflammation (by attracting phagocytes, mast cells to the focus and releasing histamine, serotonin from the latter), participation in the modification of immune complexes and their excretion from the body.
Properdin system consists of three components: protein P, or own properdin; factor B - a b-glycoprotein rich in glycine, and protease D, which is a proenzyme. Properdin is activated by bacterial endotoxin, the hormone insulin. Under its influence, factor D is activated, under the influence of which - factor B and then the complement system. Together with other humoral factors, properdin provides bactericidal, hemolytic, virus-neutralizing effects, and is a mediator of immune responses.
The humoral factors of nonspecific protection include other substances: leukins, plakins, b-lysines. Leukins are secreted by leukocytes, plakins by platelets. Both types of agents are found in blood plasma and tissue fluid and have a bacteriolytic effect. Plasma b-lysines have an even greater lytic effect on staphylococci and anaerobic microorganisms.
Many tissue fluid agents(inhibitors of hyaluronidase, phospholipases, collagenase, plasmin) inhibit the enzymatic activity of microorganisms and the vital activity of viruses.
Cellular mechanisms of nonspecific resistance. They are represented by an inflammatory reaction of tissues and phagocytosis. They involve neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, eosinophils, basophils.
tissue inflammatory response- an evolutionarily developed process of protecting the internal environment from the penetration of foreign macromolecules. Microorganisms that have penetrated into the tissue are fixed at the site of penetration, are destroyed and then removed from the tissue into the external environment with the liquid medium of the inflammation focus - exudate. Tissue cells and leukocytes entering the inflammation site form a kind of protective shaft that prevents the spread of foreign particles through the internal environment. In the focus of inflammation, the process of phagocytosis is especially effective. Phagocytosis, being a nonspecific defense mechanism, at the same time contributes to immunological defense mechanisms. This is due, firstly, to the fact that, by absorbing macromolecules and splitting them, the phagocyte, as it were, reveals the structural parts of molecules that are foreign. Secondly, phagocytosis under conditions of immunological protection proceeds faster and more efficiently. Thus, the phenomenon of phagocytosis occupies an intermediate place between the mechanisms of specific and nonspecific defense. This once again emphasizes the conditionality of dividing the mechanisms of protection of cellular homeostasis into specific and nonspecific.
End of work -
This topic belongs to:
Physiology of red blood cells
Physiology of erythrocytes .. the purpose of the lesson is to study the functions of red blood cells, the mechanisms of formation and ..
If you need additional material on this topic, or you did not find what you were looking for, we recommend using the search in our database of works:
What will we do with the received material:
If this material turned out to be useful for you, you can save it to your page on social networks:
| tweet |
All topics in this section:
Reasons for maintaining a liquid state of blood
The main task of the body in conditions of normal life is to maintain blood in a liquid state. This task is performed by the blood coagulation system. Blood can only perform its functions
Latent microcoagulation
Latent, or hidden, microcoagulation in the blood circulation occurs on a small scale continuously. In the body, blood cells are constantly destroyed and die, endothelial cells suck
Causes of intravascular thrombosis
There are many mechanisms that maintain the liquid state of the blood. However, various changes and disturbances can occur within these mechanisms. They can lead to the formation of blood clots in the
Regulation of blood clotting
Blood coagulation is regulated at three levels. At the molecular level, the stability of the content of factors is ensured. This is due to the links between the hemostasis system and the immune system.
Hemostasis system and immune system
The hemostasis system interacts with the immune system, which is especially noticeable in pathology. Thus, the hemostatic properties of endothelial cells are affected by tumor necrotizing factor-alpha, which
Hemostasis system and potentials of excitable tissues
It is known that upon excitation, the cytoplasm passes from the state of the sol to the gel. In the pauses between action potentials, the cytoplasm rapidly liquefies. Changes in the aggregate state of the plasma are explained by
The system of regulation of the aggregate state of blood and thrombohemorrhagic syndrome
The blood coagulation system is part of the functional system - the system of regulation of the aggregate state of blood (RASK system), which maintains homeostasis of the internal environment of the org.
The main components of the RASK system
central authorities. These include the bone marrow, liver, and spleen. Bone marrow produces cellular components of the hemostasis system: platelets, erythrocytes, leukocytes. in the liver with
Age-related changes in hemostasis
The blood coagulation system is formed during fetal development. The appearance of coagulation-active proteins was noted at 10-11 weeks of pregnancy. Fibrinogen appears at 4 months
Independent work of students
For independent work required: clinical centrifuge, torsion balance, water bath, stopwatch, medical tourniquet, stand with graduated and non-calibrated test tubes, pi
Work 1. Determination of blood clotting time according to Lee-White
Venous clotting time estimates the total coagulation activity of whole blood by the rate of clot formation in it. The countdown is made from the moment the first drop hits
Work 3. Determination of plasma recalcification time
Plasma recalcification time is the clotting time of citrated plasma at t 37°C after adding calcium chloride to it. This indicator, in contrast to the clotting time of the venous
Work 4. Determination of prothrombin time
Quick prothrombin time is a test that characterizes the external mechanism of blood coagulation. The basis of this test is the determination of the time of recalcification of citrate plasma in the presence of excess
Work 5. Determination of thrombin time
Thrombin time is the clotting time of citrate plasma after adding a weak concentration of thrombin solution to it. It allows you to evaluate the final phase of blood coagulation. Norm - 15-18
Work 6. Determination of the level of fibrinogen according to Rutberg
It can be determined by weighing: citrate plasma is recalcified, the resulting clot is dried with filter paper and weighed. The norm is 2-4 g / l. Increasing the content of phi
Work 7. Determination of the duration of bleeding according to Duke
The method is based on determining the bleeding time from a wound applied to the surface of the skin. standard size. This time depends on the vascular-platelet hemostatic mechanisms.
Work 8. Study of retraction of a blood clot according to Matisse
The assessment of retraction is used as one of the most important indicators of the functional activity of platelets, since contractile reactions develop only in full-fledged platelets with
Work 9. Determination of blood coagulation according to Sukharev
The principle of the method is to determine the time of spontaneous coagulation of whole capillary blood and allows you to identify a gross deficiency of coagulation factors (fibrinogen, antihemophilic globulins
Work 10. Determination of spontaneous fibrinolysis and retraction according to Kuznik
In clinical practice, it is necessary to know the resulting interaction of the components of the fibrinolytic system, since a pathological increase in fibrinolysis leads to bleeding, and a decrease - to
Means of infusion-transfusion therapy
Currently, infusion-transfusion therapy has firmly taken its own place in the treatment of various categories of patients. The most important indications for the use of this therapy in clinical
Crystalloid and colloidal solutions
They have specific properties and have gained particular importance in modern surgery and intensive care. Crystalloid (salt, electrolyte) solutions. They are easily
Photohemometry
This is a more accurate method for determining the hemoglobin content. So cyanmethemoglobin photometric method is based on the conversion of hemoglobin to cyanmethemoglobin (colored stable compound) under
Cytophotometry
This method is based on the photometric measurement of the degree of absorption of light of certain wavelengths, for example, by a suspension of erythrocytes. The percentage of delayed light is directly proportional to the number of red blood cells.
Electronic-automatic method
It is based on different principles, but the impulse principle is most often used - the difference in the electrical conductivity of blood particles and the liquid diluting them. A certain amount of diluted 0.85%
Thromboelastography
This is a method of recording the process of blood clotting and clot formation on a thromboelastograph. Principle of operation. The analyzed blood is collected directly into a cylindrical cuvette and metal is immersed in it.
Lesson 1
1. Are the statements true: a) homeostasis is the ability to maintain the constancy of the internal environment of the body, b) static processes are the basis of homeostasis, c) homeostasis is based on
Pediatric department
LESSON 1 1. Specify the sequence of stages of hematopoiesis during fetal development. 1. Splenic. 2. Mesoblastic. 3. Pechen
Lesson 2
1. Specify the differences in the composition of white blood in newborns after birth. 1. The number of leukocytes in the first 4 days after birth is higher than in adults. 2. Ney
Lesson 4
1. Are the statements true: a) in newborns, the total amount of blood is 15% of body weight, b) in adults, the total amount of blood is 20% of body weight, c) therefore, in
A) no, b) no, c) yes
SITUATIONAL TASKS 1. A person has lost 2 liters of blood. The blood group has not been established. What is the doctor's strategy? What and how much should be transfused to this recipient? 2. A patient was brought to the hospital
Answers to the questions of test control of knowledge
Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 1. 1 2. 1.2 3. 3 4. 3 5. 4 6. 2 7. 1 8. 1 9. 1 10.
Knowledge for students of the pediatric department
Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 1. 2,3,1,4 2. 1,2,3,4 3. 1,2,3 4. 1,3,4 5. 1
resistance (from lat. resistere - resist, resist) - the body's resistance to the action of extreme stimuli, the ability to resist without significant changes in the constancy of the internal environment; this is the most important qualitative indicator of reactivity;
Nonspecific resistance represents the resistance of an organism to damage (G. Selye, 1961), not to any individual damaging agent or group of agents, but to damage in general, to various factors, including extreme ones.
It can be congenital (primary) and acquired (secondary), passive and active.
Congenital (passive) resistance is determined by the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the organism (for example, the resistance of insects, turtles, due to their dense chitinous cover).
Acquired passive resistance occurs, in particular, with serotherapy, blood replacement transfusion.
Active non-specific resistance is determined by protective and adaptive mechanisms, arises as a result of adaptation (adaptation to the environment), training to a damaging factor (for example, increased resistance to hypoxia due to acclimatization to a high-altitude climate).
Nonspecific resistance is provided by biological barriers: external (skin, mucous membranes, respiratory organs, digestive apparatus, liver, etc.) and internal - histohematic (hematoencephalic, hematoophthalmic, hematolabyrinthic, hematotesticular). These barriers, as well as biologically active substances contained in fluids (complement, lysozyme, opsonins, properdin) perform protective and regulatory functions, maintain the optimal composition of the nutrient medium for the organ, and help maintain homeostasis.
FACTORS REDUCING NON-SPECIFIC RESISTANCE OF THE ORGANISM. WAYS AND METHODS TO INCREASE AND STRENGTHEN IT
Any impact that changes the functional state of regulatory systems (nervous, endocrine, immune) or executive (cardiovascular, digestive, etc.) leads to a change in the reactivity and resistance of the body.
There are known factors that reduce nonspecific resistance: mental trauma, negative emotions, functional inferiority of the endocrine system, physical and mental overwork, overtraining, starvation (especially protein), malnutrition, lack of vitamins, obesity, chronic alcoholism, drug addiction, hypothermia, colds, overheating, pain trauma, detraining of the body, its individual systems; physical inactivity, a sudden change in the weather, prolonged exposure to direct sunlight, ionizing radiation, intoxication, past illnesses, etc.
There are two groups of ways and methods that increase nonspecific resistance.
With a decrease in vital activity, loss of the ability to independent existence (tolerance)
2. Hypothermia
3. Ganglion blockers
4. Winter hibernation
While maintaining or increasing the level of vital activity (SNPS - a state of non-specifically increased resistance)
1 1. Training of the main functional systems:
physical training
hardening to low temperatures
Hypoxic training (adaptation to hypoxia)
2 2. Changing the function of regulatory systems:
Autogenic training
verbal suggestion
Reflexology (acupuncture, etc.)
3 3. Non-specific therapy:
Balneotherapy, spa therapy
Autohemotherapy
Protein therapy
Non-specific vaccination
Pharmacological agents (adaptogens - ginseng, eleutherococcus, etc.; phytocides, interferon)
To the first group include influences with the help of which stability is increased due to the loss of the body's ability to independent existence, a decrease in the activity of vital processes. These are anesthesia, hypothermia, hibernation.
When an animal in a state of hibernation is infected with plague, tuberculosis, anthrax, diseases do not develop (they occur only after it wakes up). In addition, resistance to radiation exposure, hypoxia, hypercapnia, infections, and poisoning increases.
Anesthesia contributes to an increase in resistance to oxygen starvation, electric current. In a state of anesthesia, streptococcal sepsis and inflammation do not develop.
With hypothermia, tetanus and dysentery intoxication are weakened, sensitivity to all types of oxygen starvation, to ionizing radiation decreases; increases resistance to cell damage; allergic reactions are weakened, the growth of malignant tumors slows down in the experiment.
Under all these conditions, deep inhibition occurs. nervous system and, as a result, all vital functions: the activity of regulatory systems (nervous and endocrine) is inhibited, metabolic processes are reduced, chemical reactions are inhibited, the need for oxygen decreases, blood and lymph circulation slows down, body temperature decreases, the body switches to a more ancient metabolic pathway - glycolysis. As a result of the suppression of the processes of normal vital activity, the mechanisms of active defense are also turned off (or slowed down), an unreactive state arises, which ensures the survival of the body even in very difficult conditions. At the same time, he does not resist, but only passively endures the pathogenic action of the environment, almost without reacting to it. Such a state is called portability(increased passive resistance) and is a way for the organism to survive in adverse conditions, when it is impossible to actively defend itself, it is impossible to avoid the action of an extreme stimulus.
To the second group include the following methods of increasing resistance while maintaining or increasing the level of vital activity of the organism:
Adaptogens are agents that accelerate adaptation to adverse influences and normalize stress-induced disturbances. They have a wide therapeutic effect, increase resistance to a number of factors of a physical, chemical, biological nature. The mechanism of their action is associated, in particular, with their stimulation of the synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, as well as with the stabilization of biological membranes.
By using adaptogens (and some other drugs) and adapting the body to the action of adverse environmental factors, it is possible to form a special state non-specifically increased resistance - SNPS. It is characterized by an increase in the level of vital activity, the mobilization of active defense mechanisms and functional reserves of the body, and increased resistance to the action of many damaging agents. An important condition for the development of SNPS is a dosed increase in the strength of the impact of adverse environmental factors, physical exertion, the exclusion of overloads, in order to avoid the disruption of adaptive-compensatory mechanisms.
Thus, the organism that is better, more actively resists (SNPS) or less sensitive and has greater tolerance is more resistant.
Managing the reactivity and resistance of the body is a promising area of modern preventive and curative medicine. Increasing nonspecific resistance is an effective way of general strengthening of the body.
Body resistance - (from lat. resistere - to resist ) is the property of an organism to resist the action of pathogenic factors or immunity to the effects of damaging factors of the external and internal environment. In other words, resistance is the resistance of an organism to the action of pathogenic factors.
In the course of evolution, the organism has acquired certain adaptive mechanisms that ensure its existence in conditions of constant interaction with the environment. The absence or insufficiency of these mechanisms could cause not only a violation of vital activity, but also the death of an individual.
The resistance of the body manifests itself in various forms.
Primary(natural, hereditary) ) resistanceb - this is the resistance of the organism to the action of factors, determined by the peculiarity of the structure and function of organs and tissues that are inherited. For example, the skin and mucous membranes are structures that prevent microorganisms and many toxic substances from entering the body. They perform a barrier function. Subcutaneous fat, having poor thermal conductivity, contributes to the preservation of endogenous heat. The tissues of the musculoskeletal system (bones, ligaments) provide significant resistance to deformation in case of mechanical damage.
Primary resistance may be absolute and relative :
absolute primary resistance - a classic example is hereditary resistance to a number of infectious agents ("hereditary immunity"). Its presence is explained by the molecular features of the organism, which cannot serve as a habitat for a particular microorganism, or there are no cell receptors necessary for fixing the microorganism, i.e. there is a receptor non-complementarity between aggression molecules and their molecular targets. In addition, cells may not contain substances necessary for the existence of microorganisms, or they may contain products that interfere with the development of viruses and bacteria. Due to absolute resistance, the human body is not affected by many infectious diseases of animals (absolute human immunity to rinderpest), and vice versa - animals are not susceptible to a large group of human infectious diseases (gonorrhea is a human disease only).
relative primary resistance - under certain conditions, the mechanisms of absolute resistance can change and then the body is able to interact with the agent that was previously “ignored” by it. For example, poultry (chickens) do not get sick under normal conditions. anthrax, against the background of hypothermia (cooling), it is possible to cause this disease. Camels, immune to the plague, fall ill with it after being very tired.
Secondary(acquired, modified) resistance- this is the resistance of the body, formed after the preliminary impact on it of certain factors. An example is the development of immunity after infectious diseases. Acquired resistance to non-infectious agents is formed through training for hypoxia, physical activity, low temperatures (hardening), etc.
Specific resistance – is the body's resistance to the influence of a single agent . For example, the emergence of immunity after recovery from infectious diseases such as smallpox, plague, measles. The increased resistance of the organism after vaccination also belongs to the same type of resistance.
Nonspecific resistance – is the body's resistance to exposure to multiple agents . Of course, it is impossible to achieve resistance to the whole variety of factors of the external and internal environment - they are different in nature. However, if a pathogenetic factor occurs in many diseases (caused by various ethological factors) and its action plays one of the leading roles in their pathogenesis, then resistance to it is manifested to a greater number of influences. For example, artificial adaptation to hypoxia greatly facilitates the course of a large group of pathologies, since it often determines their course and outcome. Moreover, in some cases, the resistance achieved by such a technique can prevent the development of a particular disease, pathological process.
Active resistance – it is the stability of the body, ensured by the inclusion of protective and adaptive mechanisms in response to agents . This can be the activation of phagocytosis, the production of antibodies, the emigration of leukocytes, etc. Resistance to hypoxia is achieved by increasing ventilation of the lungs, accelerating blood flow, increasing the number of red blood cells in the blood, etc.
Passive resistance – this is the stability of the body associated with its anatomical and physiological characteristics, i.e. it does not provide for the activation of reactions of the protective plan when exposed to agents. This resistance is provided by the barrier systems of the body (skin, mucous, histohematic and hematolymphatic barriers), the presence of bactericidal factors (hydrochloric acid in the stomach, lysozyme in saliva), hereditary immunity, etc.
A.Sh. Zaichik, L.P. Churilov (1999) instead of the term " passive resistance "suggest to use the term to denote the above described states of the body "portability ».
There is also a slightly different interpretation. "portability ". During the action of two or more extreme (extreme) factors, the body often responds to only one of them, and does not respond to the action of others. For example, animals exposed to radial acceleration tolerate a lethal dose of strychnine and have a higher percentage of survival under conditions of hypoxia and overheating. In shock, the body's response to mechanical stress is sharply reduced. This form of response, according to I.A. Arshavsky, cannot be named resistance , since under these conditions the body is not able to actively resist the action of other environmental agents, maintaining hemostasis, it only endures impact on the state deep oppression of vital activity . Such a state of I.A. Arshavsky and suggested calling " portability" .
General resistance – it is the resistance of an organism as a whole to the action of a particular agent. For example, general resistance to oxygen starvation ensures the functioning of its organs and systems due to various protective and adaptive mechanisms activated at various levels of organization of living systems. These are systemic reactions - an increase in the activity of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, these are also subcellular changes - an increase in the volume and number of mitochondria, etc. All this provides protection for the body as a whole.
Local resistance – is the resistance of individual organs and tissues of the body to the effects of various agents . The resistance of the mucous membranes of the stomach and duodenum to ulcer formation is determined by the state of the mucous-bicarbonate barrier of these organs, the state of microcirculation, the regenerative activity of their epithelium, etc. The availability of toxins in the CNS is largely determined by the state of the blood-brain barrier, which is impassable for many toxic substances and microorganisms.
The variety of forms of resistance demonstrates the significant capabilities of the body in protecting against the effects of external and internal environmental factors. In individuals, as a rule, one can note the presence of several types of reactivity . For example, a patient was injected with antibodies to a certain type of microorganism (staphylococcus) - the forms of resistance are as follows: secondary, general, specific, passive.
The invention relates to medicine, in particular to the therapeutic correction of functional abnormalities, characterized as a decrease in the body's resistance. The method allows to increase the effectiveness of therapeutic effects. To do this, varying subtherapeutic doses of biostimulants of plant origin are administered daily. In this case, the daily dose is determined by the law random numbers from the range of their variations, each of which differs in the amount of the drug contained in one drop of tincture, while for men under 65 years of age, variations are used, starting from the lower subtherapeutic dose; for men over 65 years of age and for women of any age, variations are selected, starting with a dose 1.5 times less than the subtherapeutic one; for children aged 1 to 4 years - start from 1/10, from 4 to 6 years - from 1/5 from 6 to 19 years - from 1/4, from 10 to 14 years - from 1/3, from 14 up to 16 years - from 1/2 subtherapeutic dose and in a satisfactory state of the body, variations of 16 doses are used, in a weakened state - from 8 doses, and in a sharply weakened state - from 4 doses. 2 s. p. f-ly, 2 tab.
FIELD: medicine. There is a known method of increasing the body's resistance by taking various biostimulants, for example, eleutherococcus, ginseng, etc. (Brehman N.N. Man and biological active substances. L. 1976; Dardymov I.V. Ginseng, eleutherococcus "M. Science, 1976). However, the known method does not take into account gender and age. Taking biostimulants, which are xenobiotics, in relatively large doses leads to a breakdown in stress, especially in weakened individuals. There is a known method of increasing the body's resistance (in the book "Adaptive reactions and body resistance" Garkavi L. Kh. Kvakina E. B. Ukolova M. A. 1990, Rostov-on-Don, p. 45), including the development of an activation reaction by a properly selected dose of a biostimulant and its systematic change (strength of exposure) towards increasing or reduction.However, this method has certain shortcomings : the selection of doses is carried out cybernetically according to the signal indicator of the reaction - the percentage of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula. Therefore, the previously proposed method requires frequent blood tests, which complicates its mass use. In addition, the blood test takes time, the desired dose change is delayed, which reduces the effectiveness of the method. The purpose of the invention is to increase the effectiveness of the therapeutic effect to increase the body's resistance, resistance to damaging effects and diseases. The goal is achieved by the fact that patients are daily administered changing subtherapeutic doses of biostimulants, using a tincture of biostimulants of plant origin, the daily dose is determined according to the law of random numbers from the range of their variations, each of which differs in the amount of the drug contained in one drop of the tincture. At the same time, for men under 65 years of age use variations starting from the lower subtherapeutic dose; for men over 65 years of age and for women of any age, variations are selected starting from a dose 1.5 times less than the subtherapeutic one; for children aged 1 to 4 - start at 1/10, 4 to 6 years from 1/5, from 6 to 10 years from 1/4, from 10 to 14 years 1/3, from 14 to 16 years with 1/2 subtherapeutic dose and in a satisfactory state of the body, variations of 16 doses are used, in a weakened state of 8 doses, and in a sharply weakened state of 4 doses; treatment is continued for a month. As a random number generator, a four-fold or three-fold, or two-fold toss of a coin is used, for each value of the combinations obtained, a certain dose of the biostimulant is fixed. To prepare doses of less than one drop, an extract diluted 10 times with water is used. The invention is new, since it is not known from the level of medicine in the field of therapeutic correction of functional abnormalities, characterized by a decrease in the body's resistance. The proposed method differs from the known ones in that the daily individual subtherapeutic dose of the stimulant is determined according to the law of random numbers and is made dependent on sex and age. A random number generator with a uniform distribution is used for four-fold and three-fold or two-fold tossing of coins, for each value of which a certain subtherapeutic dose of the stimulant is fixed. Thus, the proposed method for increasing the resistance of the body differs significantly from the known, meets the criterion of the invention "novelty". The invention has an inventive step, since for a specialist (a doctor of any specialty) it does not explicitly follow from the level of development of medicine in the field of increasing the body's resistance to various stresses and diseases and for prevention. The expediency of changing the dosage according to the law of random numbers is explained by the need to maintain the informational value of stimulation, i.e., the need to maintain the "novelty" factor during the course of exposure. Novelty is reduced due to the development of the "expectation reaction": with a daily dose according to a known scheme (in a previously known way), the body is, as it were, warned about the dose. The "novelty" factor leads to the predominance of the excitation process in the brain, and since the stimulus is small (subtherapeutic doses), the excitation develops not excessive, but moderate, physiological. The validity of this approach is also confirmed by many years of experimental studies (Garkavi L. Kh. Kvakina E. B. Ukolova M. A. 1990). It is this nature of changes in the central nervous system, as shown earlier, that is observed during the development of an activation reaction that most significantly reduces the body's resistance (Garkavi L. Kh. 1969; Kvakina E. B. 1972; Garkavi L. Kh. Kvakina E. B. Ukolova M A. 1979). The use of the law of random numbers to establish the daily dose causes the randomness of dose changes, which prevents the development of addiction and helps to preserve the "novelty factor". Thus, the proposed technical solution is not obvious, since it does not follow from the level of development in this field of medicine, it is not known either in the world or in the Russian (CIS) medical literature. The invention is industrially applicable, since the technical result achieved when using it is an increase in the body's resistance, which contributes to an increase in the level of health, the prevention of various diseases, their easier course, greater treatment efficiency, allow us to consider the method industrially applicable in various fields of medicine: for prevention, recovery, relief the course of the disease. The expediency of taking into account gender and age is associated with the high sensitivity of the body of women and the increase in sensitivity with aging. The choice of dose according to the law of random numbers (Monte Carlo method) will be considered using the example of Eleutherococcus, a single therapeutic dose of which is 30 25 drops of the extract. Starting from the maximum subtherapeutic dose, for example, from 24 drops for men under the age of 65, for example, 16 lower doses are prescribed with an interval of 1 drop (such an interval is taken for ease of practical use). In this case, each dose is numbered by a serial number, starting from N 1. Thus, each serial number corresponds to its own dose (Table 1). Women of any age and men over 65 years of age take 1.5 times less as a maximum subtherapeutic dose than for men under 65 years of age. Then the doses are signed with an interval of 1 drop. For doses smaller than a drop, an extract diluted 10 times with water (E/10) is used. To select a daily dose according to the Monte Carlo method, a "random number generator" with a uniform distribution is used. Such a generator can be: an automatic machine for obtaining random numbers, a table of random numbers, or a coin toss available to everyone. When tossing a coin, two options can be obtained: heads (O) or tails (P). To ensure the necessary randomness in the distribution of doses, it is sufficient to throw the moments three times, which gives 8 possible combinations of 3. Each of the 8 combinations is associated with one of the 8 selected subtherapeutic doses. Tossing a coin four times provides even more randomness, since it gives 16 dose options (Table 1), and twice less, since it gives 4 dose options. In the elderly and debilitated people, one should start with 3 coin tosses and use 8 minimum doses for a given sex and age of dose values, and in especially severe cases, even with 2 coin tosses and use four minimum doses. Taking into account the circadian rhythm of the called "activation reaction", the biostimulator should be taken once a day, preferably from 7 to 9 hours, when informational influence is sufficient for the formation of the named reaction. Before each intake of the biostimulator (daily, on an empty stomach, 1 time per day), it is necessary, by throwing a coin 2, 3 or 4 times, to fix the sequence of “heads” and “tails” that fell out and then determine the value of the corresponding dose according to Table 1. The criterion for choosing doses is their individualization depending on age and gender, evaluation of effectiveness - all this is based on the theory and practice of adaptive reactions that we have been developing for many years. Highly informative and well correlated with changes in the neuroendocrine and immune systems, the signal indicator of the reaction, the specially calculated leukocyte count and the total number of leukocytes, is an important criterion both for the state of the body and for evaluating the effectiveness and correctness of the selected doses. The percentage of lymphocytes determines the type of reaction (training, activation, stress), and deviations from the norm of the percentage of other elements of the blood formula (eosinophils, basophils, stab neutrophils, monocytes) and the total number of leukocytes (leukopenia or leukocytosis) indicate the presence of tension, non-physiological activation or training responses. This indicator and a change in well-being, a decrease or disappearance of complaints, and in the presence of objectively determined signs of violations, their normalization (for example, the value of blood pressure), a decrease in the number of pathogenic colonies in the autoflora of the skin in the complex allow us to judge the effectiveness of the effects. It should be noted that the above signs in the vast majority of cases (at least 90) correlate well. The fact that in the chosen prototype doses of the biostimulant "can lead to the development of stress" is simply proved: the parameters of the leukocyte formula become characteristic of stress, as the author of stress, G. Salier, found. The fact that "taking the same doses" leads to the development of an expectation reaction that reduces the therapeutic efficacy of the biostimulator is due to the fact that under any severe mode of variation in the dose (strength) of the active factor, the body is capable of extrapolation. Specifically, this is manifested by the fact that after the first change in the nature of the reaction (it can last from 2 days to a week), in the case of taking the same dose or changing the dose according to a rigid scheme, a return to the initial state (according to blood parameters) occurs, which is associated with return to the initial state according to well-being, i.e., the therapeutic effectiveness of the biostimulator is reduced or removed. The activation reaction was judged by the percentage of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula. In some people (25 people in each group), the development of the activation reaction was also judged by the autoflora of the skin. According to the proposed method, this was carried out not to select a dose, but to control (proof) the development of an activation reaction before the start of exposure and at the end of exposure, lasting for a month. The choice of a known or proposed method for obtaining an activation reaction was carried out on the basis of randomization: even dates of the onset of exposure are a known method, odd ones are proposed. The results of comparing the prototype and the proposed method showed that the proposed method effectively increases resistance in people with reduced resistance (in prenosological conditions) and causes the development of an activation reaction in a significantly higher percentage of cases. A high percentage of lymphocytes, oil, the number of pathogenic colonies in the autoflora of the skin, the disappearance of persistent complaints, improvement general condition and increased performance indicate the usefulness of the developing activation reaction (Table 2). As an example of a specific implementation of the proposed method, we present the following extracts from outpatient cards. 1. Map N 3. A 46-year-old woman, subjectively complaining of headaches, bad dream, decreased performance, fatigue, depressed mood. Objectively: the percentage of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula is 18.5, which corresponds to a stress reaction, the number of pathogenic colonies of the autoflora of the skin is 42, which is also characteristic of stress. The patient's medical examination and no specific disease was identified. Purpose: Eleutherococcus at a dose of 16 to 1 drop. Daily dose selection was made using a four-fold coin toss and then determined in accordance with the attached table. 1. In this case, for example, as a result of daily tossing of a coin, we received: Day Number of drops First OROP 10 Second RROO 3 Third RRRO -1 Fourth ORRO 9 Fifth LLCOR 14 Sixth ROOR 6 Seventh RRRR 15
Eighth RRRO 1
Ninth ORRO 9
Tenth ROOR 6
Eleventh ASRR -12
Twelfth OOOR 14
Thirteenth OROO 11
Fourteenth RROO 3
Fifteenth ASRR 12
Sixteenth ORO 13
Seventeenth ROOR 6
Eighteenth ORRR 8
Nineteenth RORR 4
20th RRRR 2
21st ORO 13
After 3 weeks of daily intake of eleutherococcus in the indicated doses, subjective improvement, disappearance of complaints, increased efficiency. The percentage of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula became 35, which corresponds to an activation reaction, the number of pathogenic skin colonies in the autoflora decreased to three, which is also characteristic of an activation reaction. 2. Map N 15
A 52-year-old man subjectively complains of pain in the region of the heart, headaches, general weakness, poor sleep, irritability, fear and anxiety, self-doubt, impotence, decreased performance. Objectively: the number of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula is 17, which corresponds to stress, the number of pathogenic colonies in the autoflora of the skin is 40, which is also characteristic of stress. Treatment was carried out with an alcoholic extract of pantocrine for 21 days at a dose of 20 to 5 drops. The choice of the daily dose was carried out according to the law of random numbers using four coin tosses in accordance with Table. one:
Day Number of drops
First OOR 20
Second RROO 13
Third ROOR 11
Fourth PPRO 8
Fifth RORO 9
Sixth ORRR 5
Seventh RORR 6
Eighth RRRR 19
Ninth OOR 18
Tenth OPOR 10
Eleventh ORRO -12
Twelfth OOOR 18
Thirteenth ORRO 12
Fourteenth RROO 13
Fifteenth RORR 11
Sixteenth RRRR 19
Seventeenth ASRR 14
Eighteenth OPOR 10
Nineteenth RRRR 7
Twentieth ASRR 14
21st ROOO 15
Three weeks later persistent complaints disappeared, increased efficiency, there was an increase in sexual potency, improved mood. Objectively: BP
125/30, the number of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula 33, which corresponds to the activation reaction, the number of pathogenic colonies in the autoflora decreased to 5, which is also characteristic of activation. 3. Map N 37
Man aged 32 years. When addressing subjectively complaints of pain in the epigastric region that occurs immediately after eating, a feeling of heaviness in this area, belching with air, poor sleep, decreased performance, fatigue, lethargy. He was treated for a long time and continues to be treated for hypoacid gastritis without a lasting effect. Objectively: the number of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula is 15; the number of colonies of pathogenic microbes is 48, which is typical (both lymphocytes and autoflora) for the stress reaction. Leuzea liquid extract treatment was prescribed at a dose of 19 to 4 drops. Choice of daily dose according to the law of random numbers by tossing a coin:
Day Number of drops
First ROOR 10
Second OOR 17
Third ROOR 10
Fourth RRRR 18
Fifth OORO 16
Sixth OOR 17
Seventh OOOR 17
Seventh RROO 12
Eighth OOOR 17
Ninth OOOO 19
Tenth ORRR 3
Eleventh ORO -16
Twelfth ORRO 11
Thirteenth RRRO 7
Fourteenth ORO 16
Fifteenth ORO -15
Sixteenth RROO 12
Seventeenth ORRR 3
Eighteenth ROOR 10
Nineteenth RRRO 7
20th RRRR 18
21st OROO 11
22nd ROOO 14
23rd RROO 12
24th PPRO 7
25th ORRO 11
26th PPRO 7
27th ASRO 16
28th OOOO 19
After 28 days persistent complaints disappeared, only sometimes there is a vague feeling of discomfort in the epigastric region, increased efficiency, improved sleep and appetite, mood. The percentage of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula 40 pathogenic colonies in the autoflora are single, which is typical for an activation reaction. Map N 7
Woman aged 49 years. When addressing complaints of pain in the heart, interruptions, weakness, fatigue, poor sleep. Objectively: BP 80/65. ECG shows right ventricular extrasystole. The number of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula is 25, which corresponds to the training reaction, the number of pathogenic colonies is 9. It was prescribed alcohol tincture ginseng root for 28 days in the dose range from 7 drops of undiluted tincture to 1 drop of tincture diluted 10 times with water. To select a daily dose, a fourfold coin toss was used, the dosage was carried out in accordance with Table. one:
Day -
First ASRR 1
Second OOR 5
Third ORRR 1 solution 1/10
Fourth ORO 3
Fifth PPRO 4
Sixth RORR 5 solutions 1/10
Seventh ROOO 2
Eighth OOOO 7
Ninth ROOO 2
Tenth RORO 5 solution 1/100
Eleventh PPRO 4 solutions 1/10
Twelfth RRRR 6
Thirteenth RROO 9
Fourteenth OOOO 7
Fifteenth PPRO 4 solutions 1/10
16th OORO 4
Seventeenth RRRR 6
Eighteenth PPRO 4 solutions 1/10
Nineteenth RROR 3 solutions 1/10
Twentieth ASRR 1
21st OOOR 5
Twenty-second ROOR 7 r-ra 1/10
23rd RORO 5 size 1/10
24th RRRR 6
Twenty-fifth OPOR 6 solutions 1/10
26th PPRO 4 solutions 1/10
27th ROOO 2
28th RORO 5 size 1/10
After 3 weeks, complaints disappeared, extrasystole was not detected on the ECG, blood pressure was 115/70, the number of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula was 43, which corresponds to an activation reaction, and there was no pathogenic flora. Map N 10
Man aged 65 years. When addressing complaints of weakness, dizziness, pain in the heart, poor sleep, memory impairment. Objectively: blood pressure is 145/90, the number of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula is 18, the number of pathogenic colonies in the autoflora of the skin is 64, which corresponds to stress. Treatment was carried out with an extract of the golden root (Rhodiola rosea), at a dose of 9 drops of the undiluted extract to 3 drops of the extract diluted 10 times with water during a month. The choice of the daily dose was carried out with the help of four coin tosses and was determined in accordance with the table, built on the same principle as Table. 1 for Eleutherococcus. In this case:
Day Number
First RROO 2
Second ASRR 3
Third OOOO 8
Fourth OORO 6
Fifth RORR 4 solutions 1/10
Sixth ORO 5
Seventh ROPP 7 solutions 1/10
Eighth ROOR 9
Ninth RRRR 8
Tenth OOOO 9
Eleventh RROO 2
Twelfth ORRO 1
Thirteenth ROOO 4
Fourteenth OROO 5
Fifteenth OROO 5
Sixteenth PPRO 6 solutions 1/10
Seventeenth ORO 6
Eighteenth PPRO 6 solutions 1/10
Nineteenth OROO 5
20th ORRO 1
21st ORO 5
22nd ASRR 3
23rd RROO 2
24th OOOR 7
25th RROO 2
26th OROO 5
Twenty-seventh ROOR 9 solution 1/10
28th RORR 4 solutions 1/10
After treatment, the patient felt a surge of strength, noted an improvement in memory, mood; pain in the heart and dizziness disappeared. AD 125/80, the number of lymphocytes 33, the number of pathogenic colonies in the autoflora of the skin 7, which corresponds to an activation reaction. In order to increase the body's resistance, the method was tested on male and female senior students daily for 15 days. The daily dose was determined by the proposed method of increasing the body's resistance according to the law of random numbers, which caused the call of the activation reaction. A four-fold coin toss was used as a random number generator, for each value of which (the sequence of four combinations of "heads" and "tails") a certain dose of the biostimulant was fixed. The subjects were divided into 2 groups. The first group received exposures with the choice of dose according to the law of random numbers, and the second group received the same dose as standard 2 times a day. In total, 166 people were tested in order to prevent colds. of which the proposed method 116, the prototype 50 people. After prophylactic exposure during the autumn-winter period for 4 months, colds in the first group (exposure according to the proposed method) were out of 116 14 people. (12), out of 50 of the prototype group, 10 people fell ill. (20). Thus, the use of biostimulants in the dosage selection mode according to the law of random numbers allows you to increase the body's resistance to a greater extent than in the prototype group when using the standard mode of exposure. The technical and economic efficiency of the proposed method for increasing the body's resistance lies in the fact that the use of the method allows to increase the body's resistance to external influences, morbidity. In addition, the method is effective for carrying out preventive and health work among the mass contingents of the population, as it is simple, affordable and does not require large material costs, as well as time.